Young, Low Mass Stars Orbiting the Galactic Center
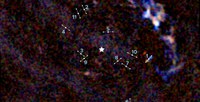
Low mass star formation was thought to be inhibited with a few parsecs of the Galactic Center by the turbulent, dense environment. Yusef-Zadeh et al., however, report the discovery of 11 bipolar outflows within a projected distance of 1 parsec of the Galactic Center, Sgr A*, based on deep ALMA observations of 13CO, H30α, and SiO (5-4) lines with sub-arcsecond spatial resolution and ~1.3 km/sec velocity resolution.
These unambiguous signatures of young protostars manifest as approaching and receding lobes of dense gas swept up by the jets created during the formation and early evolution of stars. The lobe masses and momentum transfer rates are consistent with young protostellar outflows found throughout the disk of the Galaxy. The mean dynamical age of the outflow population is estimated to be 6.5 x 103 years. The rate of star formation is ~5 × 10−4 M⊙per year, assuming a mean stellar mass of ~0.3 M⊙. This discovery provides evidence that star formation is taking place within clouds surprisingly close to Sgr A*, perhaps due to events that compress the host cloud, creating condensations with sufficient self-gravity to resist tidal disruption by Sgr A*. Low-mass star formation over the past few billion years at this level would contribute significantly to the stellar mass budget in the central few parsecs of the Galaxy. The presence of many dense clumps of molecular material within a parsec of Sgr A* suggests that star formation could take place in the immediate vicinity of supermassive black holes in the nuclei of external galaxies.
Image: Double-lobe feature produced by jets from one of the newly-forming stars. ALMA discovered 11 of these telltale signs of star formation remarkably close to the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Yusef-Zadeh et al.; B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF)
Publication: F. Yusef-Zadeh (Northwestern University) et al., ALMA Detection of Bipolar Outflows: Evidence for Low-mass Star Formation within 1 pc of Sgr A*, 2017, Astrophysical Journal Letters, 850, L30.




Connect with NRAO