First astrometric planet discovery using VLBI
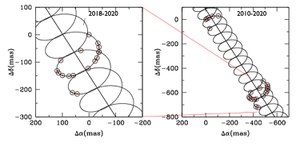 Astrometric observations of the M9 dwarf TVLM 513–46546 taken with the VLBA reveal an astrometric signature consistent with a period of 221 ± 5 days. The orbital fit implies that the companion has a mass mp = 0.35−0.42 MJ, a circular orbit (e ~ 0), a semimajor axis a = 0.28−0.31 AU, and an inclination angle i = 71°−88°. The detected companion, TVLM 513b, is one of the few giant-mass planets found associated with ultracool dwarfs. The presence of a Saturn-like planet on a circular orbit 0.3 AU from a 0.06−0.08 M ⊙ star represents a challenge to planet formation theory. This is the first astrometric detection of a planet at radio wavelengths.
Astrometric observations of the M9 dwarf TVLM 513–46546 taken with the VLBA reveal an astrometric signature consistent with a period of 221 ± 5 days. The orbital fit implies that the companion has a mass mp = 0.35−0.42 MJ, a circular orbit (e ~ 0), a semimajor axis a = 0.28−0.31 AU, and an inclination angle i = 71°−88°. The detected companion, TVLM 513b, is one of the few giant-mass planets found associated with ultracool dwarfs. The presence of a Saturn-like planet on a circular orbit 0.3 AU from a 0.06−0.08 M ⊙ star represents a challenge to planet formation theory. This is the first astrometric detection of a planet at radio wavelengths.
Figure caption: Proper motion of the star TVLM 513–46546 showing the astrometric wobble due to the presence of the planet.
Publication: Salvator Curiel (Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México) et al., An astrometric planetary companion candidate to the M9 Dwarf TVLM 513-46546, Astronomical Journal, 159, 72 (4 August 2020).
NRAO Press Release: VLBA Finds Planet Orbiting Small, Cool Star




Connect with NRAO