24B TAC Report
Summary
A total of 266 proposals were submitted to NRAO's North American facilities for semester 24B. These include the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA)/High Sensitivity Array (HSA) and the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA). Proposals are reviewed on a competitive basis with a panel review system (see Proposal Review System). Below are the statistics by proposal count and hours. The oversubscription is the ratio of the number of submitted proposals to the number of approved proposals. The pressure is the ratio of the requested time to the available time in hours. Here we only include proposals submitted for the 24B semester that have been reviewed by the NRAO TAC. We count HSA proposal hours that request the VLA as a VLBI station.
|
|
For the 24B semester, the NRAO had agreements with ALMA, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the XMM-Newton Telescope, and the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) to submit joint proposals whereby the NRAO TAC could allocate time on these external facilities (see the 24B Call for Proposals). The table below summarizes the results for all AUI North American facilities that are included in the joint program: GBT, VLBA, and VLA. The time available on the external facilities is per year, whereas the time requested and approved is only for semester 24B.
|
ALMA (hrs) |
JWST (hrs) |
HST (orbits) |
Swift (ks) |
Chandra (ks) |
XMM (ks) |
NICER (ks) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Available |
50.00 | 50.00 | 30 | 300.0 | 120.0 | 150.0 | 250.0 |
| Requested | 59.95 | 81.63 | 18 | 255.0 | 152.0 | 87.0 | 37.0 |
| Approved | 38.56 | 19.91 | 2 | 24.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 25.0 |
Telescope Pressure Plots
Pressure plots show the total hours of allocated time as a function of LST (or GST). Also shown are how the hours are divided with respect to weather conditions and observing priority. Click on the plot to enlarge.
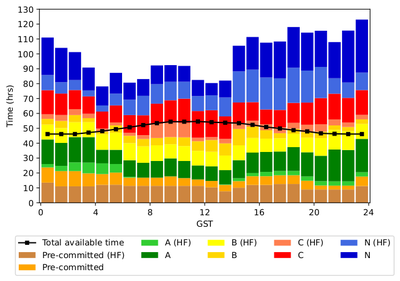
VLBA
VLBA pressure plot as a function of GST. The black line with squares is 60% of the wall-clock time available (after removing time for maintenance and sponsored time). The VLBA has two weather categories: high frequency (above 12 GHz, light shading) and low frequency (below 12 GHz, dark shading). The colors correspond to pre-committed time (brown), priority A (green), priority B (yellow), priority C (red), and priority N (blue). The shading within each priority indicates high frequencies (lower on the column) or low frequencies.
The following heuristics were used to generate the initial scheduling priorities for all sessions that are subsequently used by the TAC to derive the final priorities. Additional constraints for high frequency are in italics.
- Priority A.
- Linear rank ≤ 2.5.
- Less than 48% of the time available for scheduling (total time available minus pre-committed priority A time).
- Less than 75% of the total time available for scheduling (including pre-committed priority A time).
- Less than 75% of the high frequency time available for scheduling (including pre-committed priority A high frequency time).
- Priority B.
- Linear rank ≤ 5.0.
- Less than 96% of the time available for scheduling (total time available minus pre-committed priority A and B time).
- Less than 100% of the high frequency time available for scheduling (including pre-committed priority A and B high frequency time).
- Priority C.
- Linear rank ≤ 7.5 with < 150% of total time available or linear rank ≤ 9.0 and pressure without < 120% of the time available.
- Linear rank ≤ 7.5 for high frequency.
- Less than 125% of the high frequency time available for scheduling (including pre-committed high frequency time).
- High frequency time must be available for dynamic (or semi-dynamic) scheduling.
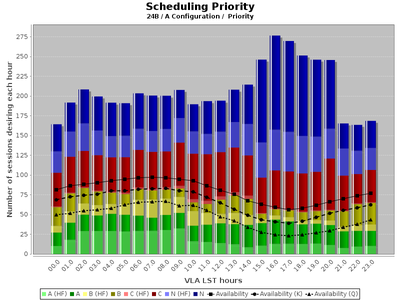
VLA
VLA Pressure plot as a function of LST. The VLA has two weather categories: high frequency (above 12 GHz, light shading) and low frequency (below 12 GHz, dark shading). The figure below show the pressure for the A-configuration. The black lines indicate the total time available for science (solid), the time available for K-band and higher frequencies (dashed), and the time available for Q-band (dotted). The letters A, B, C, and N correspond to the priorities assigned by the TAC where A and B are approved time, C is filler time, and N is rejected time.
The VLA Prioritizer is software that generates the initial scheduling priorities for all sessions that are subsequently used by the TAC to derive the final priorities. The TAC can and does change the priorities suggested by the Prioritizer. Also note that sometimes the Prioritizer cannot follow these rules strictly because of the composition of the proposals submitted. For semester 24B, the following rules were adopted as input to the VLA Prioritizer:
- Priority A is only to be considered for the top quartile of proposals.
- Priority A is only assigned if it can be given to all sessions of the proposal.
- Priority A should not to exceed 60% of available time at any LST.
- Priority (A+B) should not to exceed 92% of available time at any LST.
- Priority B should not to exceed 80% of available time in any 3h interval.
- Q band sessions will be given priority C only if linear rank is less than 1.0.
- Ku, K, Ka-band sessions will be given priority C only if linear rank is less than 3.5.
- The goal for priority C is to assign 120% of available time.
- Proposals rated worse than 9.7 will not be scheduled.
Observation Preparation
VLBA
Unless otherwise stated in the TAC comments, proposals approved for priority A time will be eligible for scheduling in semesters 24B and 25A, and proposals approved for priority B or C time will be eligible for scheduling only during semester 24B.
IMPORTANT: Those observers allocated dynamic time on the VLBA must either submit their schedule (.key) files (to vlbiobs@nrao.edu) before the beginning of the semester (1 August 2024), or contact the VLBA scheduler (schedsoc@nrao.edu) before that date to avoid a reduction in scheduling priority. Completed observing files, or preliminary ones, should be sent to the data analysts at vlbiobs@nrao.edu, for checking and possible iteration. Those proposals with fixed-date allocations (e.g. HSA proposals) will be informed of the date/time of observation about one month prior and their schedules will be due two weeks prior to observation.
IMPORTANT: Observers are cautioned that (approximately) daily observations by the United States Naval Observatory (USNO) using two stations of the VLBA (generally Hn and Mk) can interrupt open-skies observations at those stations for approximately 1 hour (see the daily-ut1 page for details).
Any approved time tabulated above may be divided into multiple scheduling blocks as appropriate, considering the scheduling priority, observing frequency, GST range suitable for the target(s), and GST pressure. For advice on preparing your scheduling blocks, please consult the VLBA Observing Guide or use the helpdesk.
VLA
Unless otherwise stated in the TAC comments, proposals approved for priority A will be considered for scheduling for two VLA configuration cycles, and proposals approved for priority B or C time become ineligible when the associated configuration ends.
IMPORTANT: The tentative start date for the A-configuration is 18 October 2024. Projects will be made available and a reminder will be sent approximately one month before the start of the configuration. Users granted dynamic, non-triggered time, must either submit their scheduling blocks before the start of the configuration or contact the VLA Scheduler (schedsoc@nrao.edu) before that date to avoid a reduction in scheduling priority. Early submission also maximizes the opportunity of them being observed and helps us to schedule the VLA most efficiently (see Configuration Plans).
In semester 24B, daytime maintenance activities peak at about 17 hours LST for the A-configuration, so observing pressure is highest there. For status of the VLA and links to the monthly schedules please see the schedsoc home page. Any approved time may be divided into multiple scheduling blocks as appropriate, considering the scheduling priority, observing frequency, LST range suitable for the target(s), and LST pressure. In order to optimize the likelihood that the project will be completed, proposers should try to maximize the LST range SBs can be observed within the approved LST range. For advice, please consult the VLA Observing Guide.
Unless stated otherwise, any time allocated is only for the identified proposal, and no modification in the project should be made without obtaining permission from NRAO scheduling staff. To seek permission, submit a ticket to the Proposal Review department of the NRAO Helpdesk.




Connect with NRAO