Performance of the VLA during the Next Semester
Resolution
Resolution
The VLA's resolution is generally diffraction-limited, and thus is set by the array configuration and frequency of observation. It is important to be aware that a synthesis array is blind to structures on angular scales both smaller and larger than the range of fringe spacings given by the antenna distribution. For the former limitation, the VLA acts like any single antenna—structures smaller than the diffraction limit (θ ∼ λ/Bmax) are not seen—with the resulting image smoothed to the resolution of the array. The latter limitation is unique to interferometers; it means that structures on angular scales significantly larger than the fringe spacing formed by the shortest baseline are not measured. No subsequent processing can fully recover this missing information, which can only be obtained by observing in a more compact array configuration, by using the mosaicking method, or by utilizing data from an instrument such as a large single antenna or a compact array comprising smaller antennas which provides this information.
Table 3.1.1 summarizes the relevant resolution information. This table shows the maximum and minimum antenna separations, the approximate synthesized beam size (full width at half-power) for the central frequency for each band, and the scale at which severe attenuation of large scale structure occurs.
| Configuration | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bmax (km1) | 36.4 | 11.1 | 3.4 | 1.03 |
| Bmin (km1) | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.0355 | 0.035 |
| Band | Synthesized Beamwidth θHPBW(arcsec)1,2,3 | |||
| 74 MHz (4) | 24 | 80 | 260 | 850 |
| 350 MHz (P) | 5.6 | 18.5 | 60 | 200 |
| 1.5 GHz (L) | 1.3 | 4.3 | 14 | 46 |
| 3.0 GHz (S) | 0.65 | 2.1 | 7.0 | 23 |
| 6.0 GHz (C) | 0.33 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 12 |
| 10 GHz (X) | 0.20 | 0.60 | 2.1 | 7.2 |
| 15 GHz (Ku) | 0.13 | 0.42 | 1.4 | 4.6 |
| 22 GHz (K) | 0.089 | 0.28 | 0.95 | 3.1 |
| 33 GHz (Ka) | 0.059 | 0.19 | 0.63 | 2.1 |
| 45 GHz (Q) | 0.043 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 1.5 |
| Band | Largest Angular Scale θLAS(arcsec)1,4 | |||
| 74 MHz (4) | 800 | 2200 | 20000 | 20000 |
| 350 MHz (P) | 155 | 515 | 4150 | 4150 |
| 1.5 GHz (L) | 36 | 120 | 970 | 970 |
| 3.0 GHz (S) | 18 | 58 | 490 | 490 |
| 6.0 GHz (C) | 8.9 | 29 | 240 | 240 |
| 10 GHz (X) | 5.3 | 17 | 145 | 145 |
| 15 GHz (Ku) | 3.6 | 12 | 97 | 97 |
| 22 GHz (K) | 2.4 | 7.9 | 66 | 66 |
| 33 GHz (Ka) | 1.6 | 5.3 | 44 | 44 |
| 45 GHz (Q) | 1.2 | 3.9 | 32 | 32 |
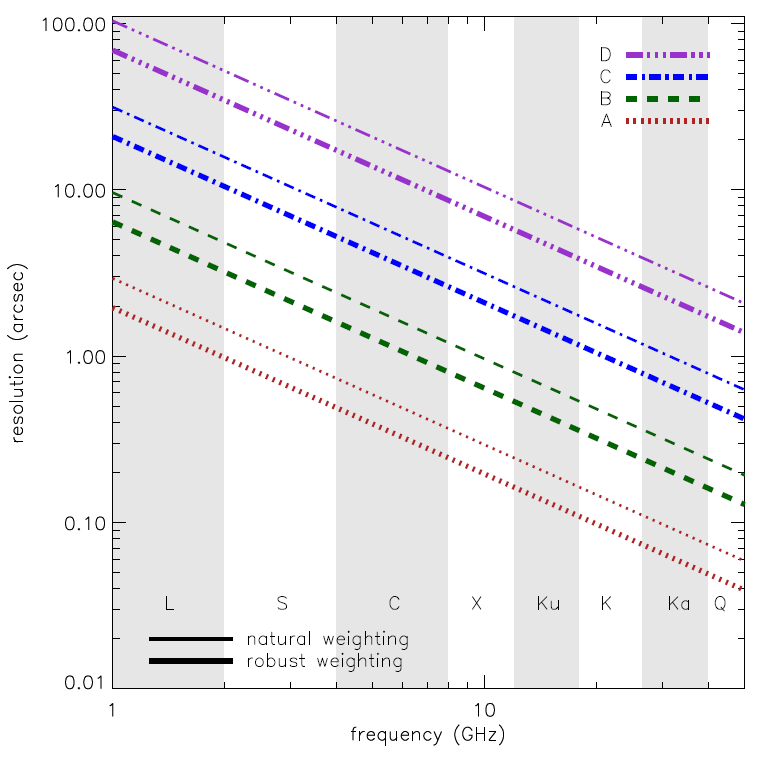
- These estimates of the synthesized beamwidth are for a uniformly weighted, untapered map produced from a full 12 hour synthesis observation of a source which passes near the zenith.
- Notes:
- 1. Bmax is the maximum antenna separation, Bmin is the minimum antenna separation, θHPBW is the synthesized beam width (FWHM), and θLAS is the largest scale structure visible to the array.
- 2. The listed resolutions are appropriate for sources with declinations between −15 and 75 degrees.
- 3. The approximate resolution for a naturally weighted map is about 1.5 times the numbers listed for θHPBW. The values for snapshots are about 1.3 times the listed values.
- 4. The largest angular scale structure is that which can be imaged reasonably well in full synthesis observations. For single snapshot observations, the quoted numbers should be divided by two.
- 5. For the C configuration, an antenna from the middle of the north arm is moved to the central pad N1. This results in improved imaging for extended objects, but may slightly degrade snapshot performance. Note that although the minimum spacing is the same as in D configuration, the surface brightness sensitivity and image fidelity to extended structure is considerably inferior to that of the D configuration.
The following figure is a graphical representation of the synthesized beamwidths for natural and robust weighting for the four main array configurations between 1 and 50 GHz. Also available are synthesized beamwidth figures for the low frequency (1–12 GHz) and the high frequency (12–50 GHz) receiver bands.
A project with the goal of doubling the longest baseline available in the A configuration, by establishing a real-time fiber optic link between the VLA and the VLBA antenna at Pie Town, was established in the late 1990s and used through 2005. This link is no longer operational; the objective of implementing a new digital Pie Town link, now that EVLA construction is complete, remains unfunded.
Sensitivity
Sensitivity
The theoretical thermal noise expected for an image using natural weighting of the visibility data is given by:
| \[\Delta I_m = \frac{SEFD}{\eta_{\rm c}\sqrt{n_{\rm pol}N(N-1)t_{\rm int}\Delta\nu}}\] | (eq. 1) |
where:
- - SEFD is the system equivalent flux density (Jy), defined as the flux density of a radio source that doubles the system temperature. Lower values of the SEFD indicate more sensitive performance. For the VLA's 25–meter paraboloids, the SEFD is given by the equation SEFD = 5.62Tsys/ηA, where Tsys is the total system temperature (receiver plus antenna plus sky), and ηA is the antenna aperture efficiency in the given band.
- - ηc is the correlator efficiency (~0.93 with the use of the 8-bit samplers).
- - npol is the number of polarization products included in the image; npol = 2 for images in Stokes I, Q, U, or V, and npol = 1 for images in RCP or LCP.
- - N is the number of antennas.
- - tint is the total on-source integration time in seconds.
- - Δν is the bandwidth in Hz.
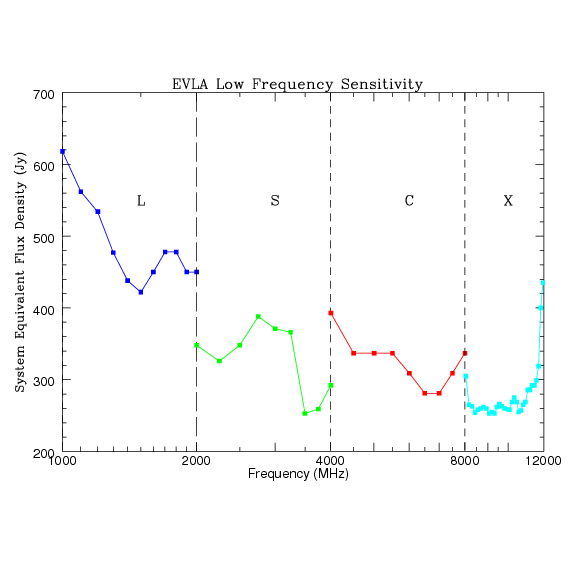
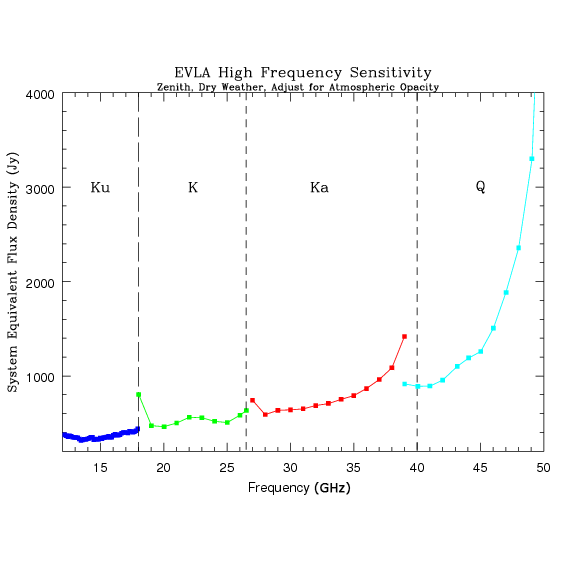
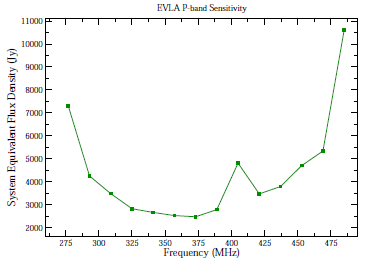
Figure 3.2.1 shows the SEFDs as a function of frequency used in the VLA exposure calculator for those Cassegrain bands currently installed on VLA antennas, and include the contribution to Tsys from atmospheric emission at the zenith. Figure 3.2.2 shows the SEFDs as a function of frequency for the P-band. These measurements are based on imaging of a field far from the galactic plane. Table 3.2.1 gives the SEFD at some fiducial VLA frequencies.
Figure 3.2.1: SEFD used in the Exposure Calculator for the VLA. Above left: The system equivalent flux density as a function of frequency for the L, S, C and X-band receivers. Right: The system equivalent flux density as a function of frequency for the Ku, K, Ka, and Q-band receivers. SEFDs at Ku, K, Ka, and Q bands include contributions from Earth's atmosphere and were determined under good conditions.
Figure 3.2.2: The SEFD used in the VLA Exposure Calculator as a function of frequency for the P-band receiver
Note that the theoretical rms noise calculated using equation 1 is the best limit possible. There are several factors that will tend to increase the noise compared with theoretical:
- For the more commonly used robust weighting scheme, intermediate between pure natural and pure uniform weightings (available in the AIPS task IMAGR and CASA task clean), typical parameters will result in the sensitivity being a factor of about 1.2 worse than the listed values.
- Confusion. There are two types of confusion: (i) that due to confusing sources within the synthesized beam, which affects low resolution observations the most. Table 3.2.1 shows the confusion noise in D configuration (see Condon 2002, ASP Conf. 278, 155), which should be added in quadrature to the thermal noise in estimating expected sensitivities. The confusion limits in C configuration are approximately a factor of 10 less than those in Table 3.2.1; (ii) confusion from the sidelobes of uncleaned sources lying outside the image, often from sources in the sidelobes of the primary beam. This confusion primarily affects low frequency observations.
- Weather. The sky and ground temperature contributions to the total system temperature increase with decreasing elevation. This effect is very strong at high frequencies, but is relatively unimportant at the other bands. The extra noise comes directly from atmospheric emission: primarily from water vapor at K-band, and from water vapor and the broad wings of the strong 60 GHz O2 transitions at Q-band.
- Losses from the 3-bit samplers. The VLA's 3-bit samplers incur an additional 10–15% loss in sensitivity above that expected—i.e., the efficiency factor ηc = 0.78 to 0.83.
| Frequency | SEFD (Jy) | RMS confusion level in D config (µJy/beam) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.39 GHz (P) | 2790 | 4200 | ||
| 1.5 GHz (L) | 420 | 89 | ||
| 3.0 GHz (S) | 370 | 14 | ||
| 6.0 GHz (C) | 310 | 2.3 | ||
| 10.0 GHz (X) | 250 | negligible | ||
| 15 GHz (Ku) | 350 | negligible | ||
| 22 GHz (K) | 560 | negligible | ||
| 33 GHz (Ka) | 710 | negligible | ||
| 45 GHz (Q) | 1260 | negligible |
In general, the zenith atmospheric opacity to microwave radiation is very low: typically less than 0.01 at L, C, and X-bands; 0.05 to 0.2 at K-band; and 0.05 to 0.1 at the lower half of Q-band, rising to 0.3 by 49 GHz. The opacity at K-band displays strong variations with time of day and season, primarily due to the 22 GHz water vapor line. Observing conditions are best at night and in the winter. Q-band opacity, dominated by atmospheric O2, is considerably less variable.
Observers should remember that clouds, especially clouds with large water droplets (thunderstorms), can add appreciable noise to the system temperature. Significant increases in system temperature can, in the worst conditions, be seen at frequencies as low as 5 GHz.
Tipping scans—which are currently unavailable but will be implemented at some time in the future—can be used for deriving the zenith opacity during an observation. In general, tipping scans should only be needed if the calibrator used to set the flux density scale is observed at a significantly different elevation than the range of elevations over which the complex gain calibrator (amplitude and phase) and target source are observed.
When the flux density calibrator observations are within the elevation range spanned by the science observing, elevation dependent effects (including both atmospheric opacity and antenna gain dependencies) can be accounted for by fitting an elevation-dependent gain term. See the following items:
- Antenna elevation-dependent gains. The antenna figure degrades at low elevations, leading to diminished forward gain at the shorter wavelengths. The gain-elevation effect is negligible at frequencies below 8 GHz. The antenna gains can be determined by direct measurement of the relative system gain using the AIPS task ELINT on data from a strong calibrator which has been observed over a wide range of elevation. If this is not possible, care should be taken to observe a primary flux calibrator at the same elevation as the target.
Both CASA and AIPS allow the application of elevation-dependent gains and an estimated opacity generated from ground-based weather through the CASA tasks gencal and plotweather, and AIPS task INDXR.
- Pointing. The SEFD quoted above assumes good pointing. Under calm, nighttime conditions, the antenna blind pointing is about 10 arcsec rms. The pointing accuracy in daytime can be much worse—occasionally exceeding 1 arcminte due to the effects of solar heating of the antenna structures. Moderate winds have a very strong effect on both pointing and antenna figure. The maximum wind speed recommended for high frequency observing is 11 mph (5 m/s). Wind speeds near the stow limit 45 mph (20 m/s) will have a similar negative effect at 8 and 15 GHz.
To achieve increased pointing accuracy, referenced pointing is recommended where a nearby calibrator is observed in interferometric pointing mode every hour or so. The local pointing corrections measured can then be applied to subsequent target observations. This reduces rms pointing errors to as little as 2–3 arcseconds (but more typically 5–7 arcseconds) if the reference source is within about 15 degrees in azimuth and elevation of the target source and the source elevation is less than 70 degrees. At source elevations greater than 80 degrees (zenith angle < 10 degrees), source tracking becomes difficult; it is recommended to avoid such source elevations during the observation preparation setup.
Use of referenced pointing is highly recommended for all Ku, K, Ka, and Q-band observations, and for lower frequency observations of objects whose total extent is a significant fraction of the antenna primary beam. It is usually recommended that the referenced pointing measurement be made at 8 GHz (X-band), regardless of what band your target observing is at, since X-band is the most sensitive and the closest calibrator is likely to be weak. Proximity of the reference calibrator to the target source is of paramount importance; ideally the pointing sources should precede the target by 20 or 30 minutes in Right Ascension (RA). The calibrator should have at least 0.3 Jy flux density at X-band and be unresolved on all baselines to ensure an accurate solution.
To aid VLA proposers there is an online guide to the exposure calculator; the exposure calculator provides a graphical user interface to these equations.
Special caveats apply for P-band (230–470 MHz) observing. The SEFD's in Figure 3.2.2 or that listed in table 3.1.2 are from an observation taken far from the Galactic plane, where the sky brightness is about 30K. At P-band, Galactic synchrotron emission is very bright in directions near the Galactic plane. The system temperature increase due to Galactic emission will degrade sensitivity by factors of two to three for observations in the plane, and by a factor of five or more at or near the Galactic center. Additionally, the antenna efficiency (currently about 0.31 for 300 MHz) will decline with both increasing and decreasing frequencies from the center of P-band.
The beam-averaged brightness temperature measured by a given array depends on the synthesized beam, and is related to the flux density per beam by:
| \[T_{\rm b} = \frac{S \lambda^2}{2k\Omega} = F \cdot S\] | (eq. 2) |
where Tb is the brightness temperature (Kelvins) and Ω is the beam solid angle. For natural weighting (where the angular size of the approximately Gaussian beam is ∼1.5λ/Bmax), and S in mJy per beam, the parameter F depends on the synthesized beam, therefore on the array configuration, and has the approximate value of F = 190, 18, 1.7, 0.16 for A, B, C, and D configurations, respectively. The brightness temperature sensitivity can be obtained by substituting the rms noise, ΔIm, for S. Note that Equation 2 is a beam-averaged surface brightness; if a source size can be measured, then the source size and integrated flux density should be used in Equation 2 and the appropriate value of F calculated. In general, the surface brightness sensitivity is also a function of the source structure and how much emission may be filtered out due to the sampling of the interferometer. A more detailed description of the relation between flux density and surface brightness is given in Chapter 6 of Reference 1, listed in Documentation.
For observers interested in HI in galaxies, a number of interest is the sensitivity of the observation to the HI mass. This is given by van Gorkom et al. (1986; AJ, 91, 791):
| \[M_{\rm HI} = 2.36 \times 10^5 D^2 \sum S \Delta V ~~~~M_\odot\] | (eq. 3) |
where D is the distance to the galaxy in Mpc, and SΔV is the HI line area in units of Jy km/s.
VLA Frequency Bands and Tunability
-
- 1. Listed here are the nominal band edges. For all bands, the receivers can be tuned to frequencies outside this range, but at the cost of diminished performance. Contact the NRAO Helpdesk for further information.
- 2. The 4-band system is currently under development. Observing time may be requested through the RSRO program.
- 3. The default setup for P-band will provide 16 subbands from the A0/C0 IF pair, each 16 MHz wide, to cover the frequency range 224–480 MHz. The channel resolution is 125 kHz.
- 4. The default frequency setup for L-band comprises two 512 MHz IF pairs (each comprising 8 contiguous subbands of 64 MHz) to cover the entire 1–2 GHz of the L-band receiver.
Tuning Restrictions
In general, for all frequency bands except Ka, if the total span of the two independent IF pairs of the 8-bit system (defined as the frequency difference between the lower edge of one IF pair and the upper edge of the other) is less than 8.0 GHz, there are no restrictions on the frequency placements of the two IF pairs. For K, Ka, and Q-bands—the only bands where a span greater than 8 GHz is possible—there are special rules:
- At Ka-band, the low frequency edge of the A0/C0 IF pair must be greater than 32.0 GHz. There is no restriction on the B0/D0 frequency, unless the B0/D0 band overlaps the A0/C0 band when the latter is tuned at or near the 32.0 GHz limit. In this case, the Observation Preparation Tool (OPT) may not allow the requested frequency setups. Users wanting to use such a frequency setup are encouraged to contact the NRAO Helpdesk for possible tuning options.
- At K and Q-bands, if the frequency span is greater than 8.0 GHz, the B0/D0 frequency must be lower than the A0/C0 frequency.
For the 3-bit system, the maximum frequency span permitted for the A1/C1 and A2/C2 IF pairs is about 5000 MHz. The same restriction applies to B1/D1 and B2/D2. The tuning restrictions given above for the separation and location of the 8-bit pairs A0/C0 and B0/D0 also apply to the 3-bit pairs, with A0/C0 replaced by A1/C1 and A2/C2, and B0/D0 replaced by B1/D1 and B2/D2.
VLA Samplers
The VLA is equipped with two different types of samplers, 8-bit with 1GHz bandwidth, and 3-bit with 2GHz bandwidth. The choice depends on your science goals and on technicalities described below.
The 8-bit Set consists of four 8-bit samplers running at 2.048 GSamp/sec. The four samplers are arranged in two pairs, each pair providing 1024 MHz bandwidth in both polarizations. The two pairs are denoted A0/C0 and B0/D0. Taken together, the four samplers offer a maximum of 2048 MHz coverage with full polarization. The frequency spans sampled by the two pairs need not be adjacent. Some restrictions apply, depending on band, as described in the section on Frequency Bands and Tunability.
The 3-bit Set consists of eight 3-bit samplers running at 4.096 GSamp/sec. The eight samplers are arranged as four pairs, each pair providing 2048 MHz bandwidth in both polarizations. Two of these pairs, denoted A1/C1 and A2/C2 cannot span more than 5000 MHz (lower edge of one to the higher edge of the other). The same limitation applies to the second pair, denoted B1/D1 and B2/D2. The tuning restrictions are described in the section on Frequency Bands and Tunability.
Which set to use?
- S, L, and 4/P-band observations, whether line or continuum, should use the 8-bit sampler set.
- C and X-band continuum observations should use 3-bit samplers in order to exploit the full 4 GHz bandwidth: in spite of the 15% reduction in sensitivity that comes with 3-bit (at equal bandwidth to the 8-bit samplers—see below for details) and the reduced effective bandwidth after removing RFI, this still provides superior overall sensitivity. For more details we refer to EVLA memo 166.
- Ku, K, Ka, and Q-band continuum observations should use the 3-bit samplers for maximum bandwidth.
- Wide-band spectral line searches requiring more than 2 GHz span should use the 3-bit samplers.
- Spectral-line observations which fit within two, possibly disjoint, 1 GHz bands should use the 8-bit set.
- Simultaneous continuum and high resolution spectral line observation can use mixed 3-bit and 8-bit samplers. The 3-bit samplers in this case will be set up to deliver the continuum data, while the 8-bit samplers will be for the spectral line data. This mix mode can be used in C-band and higher.
Major Characteristics of each Set
The 8-bit samplers are warranted for observations at 4/P, L, and S-bands. The full analog bandwidth from the receivers fits within the 2048 MHz span covered by the samplers.
For the 3-bit samplers, users need to be aware of the following issues:
- Sensitivity: compared to the 8-bit system, the sensitivity of the 3-bit samplers is worse by ~15% (at equal bandwidth). Alternatively, a given continuum noise level requiring on-source integration time T with the 8-bit (two bands of 1GHz), requires 0.33T with the 3-bit (4 bands of 2GHz, assuming the bandwidth is available from the front end).
- Resonances: each of the eight 3-bit samplers on an antenna has a resonance about 3 MHz wide. Each resonance is independent of all others, so there is no correlated signal between antennas. The resonance degrades the spectrum in its narrow frequency range, but has little effect on continuum observing. Bandpass solutions will be affected, but can be interpolated over. Spectral-line calibration and images at the affected frequencies will show significant loss in sensitivity. The resonances are easily seen in autocorrelation spectra, and it is recommended that users, especially spectral-line users, utilize these to locate the compromised frequencies.
- Amplitude Calibration: The traditional method for both 8- and 3-bit systems is to observe a flux-density calibrator, use self-cal to determine the antenna amplitude calibration factors (gains), and transfer the gains to the phase calibrator and target. For 3-bit samplers this procedure gives results good to 5% between elevations of 20–70 degrees. (Expect worse at the upper edge of Q-band and/or during bad weather.) The switched power data can be used to correct for system gain variations and works well for the 8-bit samplers. For 3-bit samplers, the Pdif depends on the Psum, i.e., Pdif is non-linear and its application will bias the resulting visibilities by 5–10%. The origin of this effect is understood, but we have not yet determined how best to compensate for it. Because of this, we do not recommend use of the Psum and Pdif data to calibrate visibilities from the 3-bit samplers. We do, however, recommend that the requantizer gains in the switched power data be applied to remove gain changes. For more information about the switched power, Psum, and Pdif, see EVLA memo 145.
Setting up the 8-bit or 3-bit Samplers
Either set requires an initial scan for each individual LO (frequency) tuning, during which power levels are optimized.
For the 8-bit system, a dummy scan of 1 minute duration is sufficient for each tuning. This is usually done while the antennas are slewing at the start of an observing file, as the pointing direction of the antennas is not critical.
For the 3-bit system, the requirements are more demanding, see the section on 3-bit setup within the Guide to Observing with the VLA. The minimum setup time is 1 minute for each tuning to adjust the power levels and bandpass slopes across the 2GHz samplers. These values are retained and applied if the tuning is re-encountered in the same observation. Additionally, every time the LO setup is changed—whether or not it is new (e.g., changing from 8-bit X-band reference pointing back to target)—a scan of 30 seconds is needed to reset the subband gains (requantizers) in the correlator. For better amplitude calibration at high frequencies, the 3-bit initial setup should be near the elevation of the target, so do it after the first 8-bit setup described above. For 3-bit observing without 8-bit (e.g., C or X-band without reference pointing), the power variation with elevation is small, so the 3-bit setup can be done at any elevation.
For settings that use a mix of 3-bit and 8-bit samplers, the guidelines to set up the 3-bit samplers should be followed.
Other issues
The overhead for setup of 3-bit samplers can eat into observing time, especially for projects with many different LO settings, and/or sources all over the sky accompanied by band change, reference pointing, and requantizer reset for each direction. The impact is most severe for short scheduling blocks.
Polarization testing conducted so far indicates no degradation of performance by using the 3-bit samplers.
Time Resolution and Data Rates
The default integration times for the various array configurations and frequency bands are as follows:
| Configurations | Observing Bands | Default integration time |
|---|---|---|
| A, B, C, D | P | 2 seconds |
| A | L S C X Ku K Ka Q | 2 seconds |
| B | L S C X Ku K Ka Q | 3 seconds |
| C, D | X Ku K Ka Q | 3 seconds |
| C, D | L S C | 5 seconds |
Observations with the 3-bit (wideband) samplers, when applicable, must use these integration times. Observations with the 8-bit samplers may use shorter integration times, but these must be requested and justified explicitly in the proposal, and obey the following restrictions:
| Proposal type |
Minimum integration time | Maximum data rate |
|---|---|---|
| General Observing (GO) and Shared Risk Observing (SRO) |
50 msec | 25 MB/s (90 GB/hr), or up to 60 MB/s (216 GB/hr) with additional justification |
| Resident Shared Risk Observing (RSRO) | < 50 msec | > 60 MB/s (216 GB/hr) |
Note that integration times as short as 5 msec and data rates as high as 300 MB/s can be supported for some observing, though any such observing is considered Resident Shared Risk Observing (RSRO). For these short integration times and high data rates there will be limits on bandwidth and/or number of antennas involved in the observation. Those desiring to utilize such short integration times and high data rates should consult with NRAO staff.
The maximum recommended integration time for any VLA observing is 60 seconds. For high frequency observations with short scans, e.g., fast switching (as described in Rapid Phase Calibration and the Atmospheric Phase Interferometer (API)), shorter integration times may be preferable.
Observers should bear in mind the data rate of the VLA when planning their observations. For Nant antennas and integration time Δt, the data rate† is:
| Data rate | ~ 45 MB/sec × (Nchpol/16384) × Nant × (Nant − 1)/(27×26) / (Δt/1 sec) |
| ~ 160 GB/hr × (Nchpol/16384) x Nant × (Nant − 1)/(27×26) / (Δt/1 sec) | |
| ~ 3.7 TB/day × (Nchpol/16384) × Nant × (Nant − 1)/(27×26) / (Δt/1 sec) | |
| ...equation (4) |
Here Nchpol is the sum over all subbands of spectral channels times polarization products:
| Nchpol = Σsb Nchan,i × Npolprod,i |
where Nchan,i is the number of spectral channels in subband i, and Npolprod,i is the number of polarization products for subband i (1 for single polarization [RR or LL], 2 for dual polarization [RR and LL], 4 for full polarization products [RR, RL, LR, LL]). This formula, combined with the maximum data rates given above, imply that observations using the maximum number of channels currently available (16384) will be limited to minimum integration times of ~2 seconds for standard observations, and 0.8 seconds for shared risk observations.
These data rates are challenging for transfer and analysis. Data may either be downloaded via ftp over the Internet, or mailed on hard drives for large data sets or for those with slow Internet connections (please review the data shipping policy). For users whose science permits, the Archive Access Tool allows some level of frequency averaging in order to decrease data set sizes before ftp; note that the full spectral resolution will be retained in the NRAO archive for all observations.
Higher time resolutions and data rates are possible in principle but will be considered only through the Resident Shared Risk Observing program.
†Note: The data rate formula given above does not account for the auto-correlations delivered by WIDAR. Precise data rate values can be obtained through the use of the General Observing Setup Tool (GOST), or the Resource Catalog Tool (also known as the Instrument Configuration Tool) of the Observation Preparation Tool (OPT).
Radio Frequency Interference
The very wide bandwidths of the VLA mean that radio frequency interference (RFI) will be present in a far larger fraction of current observations than in observations made with the old systems. Considerable effort has gone into making the VLA's electronics as linear as possible, so that the effects of any RFI will remain limited to the actual frequencies at which the RFI exists. Non-linear effects, such as receiver saturation, should occur only for those very unlikely, and usually very brief, times when the emitter is within the antenna primary beam.
RFI is primarily a problem within the low frequency (C, S, L, and the low-band system) bands, and is most serious in the D configuration. With increasing frequency and increasing resolution comes an increasing fringe rate, which is often very effective in reducing interference to tolerable levels.
The bands within the tuning range of the VLA which are allocated exclusively to radio astronomy are: 1400–1427 MHz, 1660–1670 MHz, 2690–2700 MHz, 4990–5000 MHz, 10.68–10.7 GHz, 15.35–15.4 GHz, 22.21–22.5 GHz, 23.6–24.0 GHz, 31.3–31.8 GHz, and 42.5–43.5 GHz. No external interference should occur within these bands.
VLA staff periodically observes the entire radio spectrum with the VLA, from 1.0 through 50.0 GHz with 125 kHz channel resolution, to monitor the ever-changing RFI spectrum. Users concerned about the precise frequencies of strong RFI, and the likelihood of being affected, are encouraged to peruse these plots. To access these plots, or for more information on RFI, including the impact of satellite transmissions, please see the RFI section in the Guide to Observing with the VLA.
Subarrays
The continuum subarray option offers two 1 GHz baseband pairs with the 8-bit samplers in up to 3 subarrays, with the same spectral channel and polarization product options as are available for wideband observing. The setup for each subarray is completely independent in terms of observing frequency, polarization products, and integration times.
When using three subarrays, there are some restrictions on the number of antennas in each subarray. The Baseline Board in the correlator treats each set of 4 antennas independently, using a separate column of correlator chips. With 8 such columns, the correlator can handle up to 8×4 = 32 antennas. The correlator configuration software requires that a given column not be split across subarrays. This does not matter when using only two subarrays, but forces some subtle restrictions when using three. For instance, one cannot observe with 9 antennas in each of 3 subarrays, because 9 antennas requires three columns (two with 4 antennas each, and one with 1 antenna); three subarrays of 9 antennas each would require 3×3 = 9 columns, one more than are actually available. Splitting the array into 10, 9, and 8 antennas is allowed, since the first two subarrays use 3 columns each, while the third uses only two.
Table 3.8.1 gives four examples of how correlator resources can be split into multiple subarrays. Antennas in each subarray are color-coded: red for subarray 1, green for subarray 2 (if present), and blue for subarray 3 (if present). The last column gives the number of antennas in each subarray (e.g., in the setup shown in the first row, subarray 1 has 10 antennas, subarray 2 has 9 antennas, and subarray 3 has 8 antennas). In all cases a total of 27 antennas are used. The columns are numbered in reverse order (C7 to C0) to match the numbering scheme used on the actual Baseline Boards.
| Number of antennas correlated using each Baseline Board column | Number of antennas | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | C0 | |
| 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 10 + 9 + 8 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 14 + 13 |
| 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 11 + 11 + 5 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | — | 27 |
For more information on subarrays, please see the Subarray section in the Guide to Observing with the VLA.
Positional Accuracy & Astrometry
The position of a target can be determined to a small fraction of the synthesized beam, limited by atmospheric phase stability, the proximity of an astrometric calibrator, the calibrator-source cycle time, and the SNR on target.
In preparation for observing, the a priori position must be known to within the antenna primary beam, except perhaps for mosaicking observations. In the special case of using the phased VLA as a VLBI element, the a priori position must be accurate to within the synthesized beam of the array.
In post-processing, target positions are typically determined from an image made after phase calibration, i.e., correcting the antenna and atmospheric phases as determined on the reference source. The accuracy of the calibration determines the accuracy of the positions in the image. Note that phase self-calibration imposes the assumed position of the model, i.e., makes the position indeterminate. Therefore, an absolute position cannot be determined after self-calibration, but relative positions between features within a self-calibrated image are valid.
It may help to think of astrometry as two methods, narrow-field and wide-field.
Narrow-field astrometry
In narrow-field astrometry, the target is close to the phase tracking center and the antennas nod every few minutes between the target and a calibrator. Under good conditions of phase stability with accurate antenna positions (baselines), a strong target, a close calibrator with accurately known position, and rapid switching, the accuracy can approach 1–2% of the synthesized beam, with a floor of ~2 milliarcseconds (mas). Even under more typical conditions, 10% of the beam is readily achieved.
Astrometric calibrators are marked J2000 A in the VLA calibrator list, and have an accuracy of ~2 mas. Other catalogs from the USNO and the VLBA are also useful, but offsets may exist between the VLA and VLBA centroids arising from extended structure in the particular source and the different resolutions of the arrays.
For studies of proper motion and parallax, the absolute accuracy of a calibrator may be less important than its stability over time. Close, or in-beam calibrators with poor a priori positions, can be used and tied to the ICRF reference frame in the same or separate observations.
Phase stability can be assessed in real time from the Atmospheric Phase Interferometer (API) at the VLA site, which uses observations of a geostationary satellite at ~12 GHz. Dynamic scheduling uses the API data to run a project under suitable conditions specified by the user. VLBI projects using the phased VLA will typically be fixed date and not dynamically scheduled.
Wide-field astrometry
Wide-field astrometry is used to determine the positions of targets within the primary beam, referenced to a calibrator within the beam or close by. In addition to the previous effects, there are distortions as a function of position in the field, from small errors in the Earth Orientation Parameters (EOP) used at correlation time, differential aberration, and phase gradients across the primary beam. With no special effort, the errors build up to roughly one synthesized beam at a separation of ~104 beams from the phase tracking center. Not all these errors are fully understood, and accurate recovery of positions over the full primary beam in the wide-band, wide-field case is a research area. These effects are handled somewhat differently in the post-processing packages. Check with VLA staff for more details via the NRAO Helpdesk.
Calibration and Flux Density Scale
The VLA Calibrator List contains information on 1860 sources sufficiently unresolved and bright to permit their use as calibrators; and is also available from within the Observation Preparation Tool (OPT).
Accurate flux densities can be obtained by observing one of 3C286, 3C147, 3C48 or 3C138 during the observing run. Not all of these are suitable for every observing band and configuration—consult the Guide to Observing with the VLA for advice. Over the last several years, accurate source models have been implemented directly in AIPS and CASA for much improved calibration of the amplitude scales. Models are available for 3C48, 3C138, 3C147, and 3C286 at L, S, C, X, Ku, K, Ka, and Q-bands.
Since the standard source flux densities are slowly variable, we monitor their flux densities when the array is in its D configuration. As the VLA cannot accurately measure absolute flux densities, the values obtained must be referenced to assumed or calculated standards as described in the next paragraph. Table 3.11.1 shows the flux densities of these sources in January 2012 at the standard VLA bands. The flux density scale for the VLA, from 1 through 50 GHz, is based on emission models of the planet Mars, which is then calibrated to the CMB dipole using WMAP (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe) observations (for details see Perley and Butler, 2013a). The source 3C286 (J1331+3030) is known to be non-variable, and has thus been adopted as the prime flux density calibrator source for the VLA. The adopted polynomial expression for the spectral flux density for 3C286 is:
\[\log(S) = 1.2515 - 0.4605 \log(f) - 0.1715 \log^2(f) + 0.0336 \log^3(f)\]
where S is the flux density in Jy, and f is the frequency in GHz.
The absolute accuracy of our flux density scale is estimated to be about 2%. With care, the internal accuracy in flux density bootstrapping is better than 1% at all bands except Q-band, where pointing errors limit bootstrap accuracy to perhaps 3%. Note that such high internal accuracies are only possible in long-duration observations where the antenna gain curves and atmospheric opacity can be directly measured, and where there is good elevation overlap between the target source(s) and the flux density standard calibrator.
| Source |
1465 MHz | 2565 MHz | 4885 MHz | 8435 MHz | 14965 MHz | 22460 MHz | 36435 MHz | 43340 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3C48 = J0137+3309 | 15.56 | 9.80 | 5.39 | 3.14 | 1.77 | 1.19 | 0.73 | 0.63 |
| 3C138 = J0521+1638 | 8.71 | 6.17 | 4.02 | 2.78 | 1.89 | 1.46 | 1.03 | 0.92 |
| 3C147 = J0542+4951 | 21.85 | 13.75 | 7.59 | 4.49 | 2.59 | 1.77 | 1.10 | 0.94 |
| 3C286 = J1331+3030 | 14.90 | 10.03 | 7.34 | 5.09 | 3.39 | 2.52 | 1.75 | 1.53 |
| 3C295 = J1411+5212 | 22.15 | 12.95 | 6.41 | 3.34 | 1.62 | 0.957 | 0.507 | 0.403 |
| NGC7027 | 1.62 | 3.59 | 5.38 | 5.79 | 5.62 | 5.42 | 5.18 | 5.04 |
The sources 3C48, 3C147, and 3C138 are all slowly variable. VLA staff monitor these variations on timescales of a year or two; suitable polynomial coefficients are determined for them which should allow accurate flux density bootstrapping. These coefficients are updated approximately every other year and are used in the AIPS task SETJY and in the CASA task setjy.
The VLA antennas have elevation-dependent gain variations which are important to account for at the four highest frequency bands. Gain curves are determined by VLA staff, and the necessary corrections are applied to the visibility data when these data are downloaded from the archive. Additionally, atmospheric opacity will also cause an elevation-dependent gain which is also particularly notable at these four highest frequency bands. Currently, we do not have an atmospheric opacity monitoring procedure; users should utilize the appropriate tasks available in both AIPS and CASA to estimate and correct for the opacity using ground-based weather data. Correction of these gain dependencies, plus regular calibration using a nearby phase calibrator, should enable good amplitude gain calibration for most users. Please note that extraordinary attenuation by clouds can only be approximately corrected for by regular observation of a nearby calibrator.
A better procedure for removing elevation gain dependencies uses the AIPS task ELINT. This task will generate a 2nd order polynomial gain correction utilizing your own calibrator observations. This will remove both the antenna and opacity gain variations, and has the decided advantage of not utilizing opacity models or possibly outdated antenna gain curves. Use of this procedure is only practical if your observations span a wide range in elevation.
By far the most important gain variation effect is that due to pointing. Daytime observations on sunny days can suffer pointing errors, primarily in elevation, of up to one arcminute. This effect can be largely removed by utilizing the referenced pointing procedure which determines the pointing offset of a nearby calibrator. This offset is then applied to subsequent target source observations. It is recommended that this local offset be determined at least hourly, utilizing an object within 15 degrees of the target source—preferentially at an earlier R.A.. Studies show that the maximum pointing error will be reduced to about 7 arcseconds or better. VLA staff continue to work on improving this essential methodology.
The VLA's post-amplifiers are not temperature stabilized and exhibit significant gain changes between night and day, particularly at the four highest frequency bands. Changes as large as 30% have been seen between night and day in calm, clear conditions. These gain changes, and others caused by possible changes in attenuator settings, are monitored and will be removed with excellent accuracy by application of the internal calibration signal, whose results are recorded in the switched power table (SY table in AIPS). These corrections are not applied by default—users who wish to correct for these gain changes must utilize the appropriate tasks in AIPS or CASA. For the most accurate flux density bootstrapping, this table must be applied to the visibility data before calibration. Gain bootstrapping better than 1% can be accomplished for the 8-bit sampler system after application of the switched power data. For the 3-bit system there is an additional complication, as the values of the switched power data are sensitive to the total power as well as the system gain. VLA staff are currently working on a methodology to remove the total power dependency. Not applying the switched power data will reduce bootstrapping accuracy to perhaps 10%, and possibly worse, if the observation of the flux density calibrator is not close in time to the local complex gain calibrator (amplitude and phase).
Complex Gain Calibration
General Guidelines for Gain Calibration
Adequate gain calibration is a complicated function of source-calibrator separation, frequency, array scale, and weather. Since what defines adequate for some experiments is completely inadequate for others, it is difficult to define simple guidelines to ensure adequate phase calibration. However, some general statements remain valid most of the time. These are given below.
- Under decent conditions with no thunderstorms or ionospheric storms, tropospheric effects dominate at frequencies higher than about 4 GHz; ionospheric effects dominate at frequencies lower than about 4 GHz.
- Atmospheric (troposphere and ionosphere) effects are nearly always unimportant in the C and D configurations at L and S-bands, and in the D configuration at X and C-bands. For these cases, calibration need only be done to track instrumental changes—a couple of times per hour is usually sufficient.
- If your target object has sufficient flux density to permit phase self-calibration, there is no need to calibrate more than once hourly at low frequencies or 15 minutes at high frequencies in order to track pointing or other effects that might influence the amplitude scale. The enhanced sensitivity of the VLA guarantees, for full-band continuum observations, that every field will have enough background sources to enable phase self-calibration at L and S-bands. At higher frequencies, the background sky is not sufficient, and only the flux of the target source itself will be available.
- The smaller the source-calibrator angular separation, the better. In deciding between a nearby calibrator with an S code in the calibrator database, and a more distant calibrator with a P code, the nearby calibrator is usually the better choice. A detailed description of calibrator codes is available in the calibrator list.
- In clear and calm conditions, most notably in the summer, phase stability often deteriorates dramatically after about 10AM due to small-scale convective cells set up by solar heating. Observers should consider a more rapid calibration cycle for observations between this time and a couple hours after sundown.
- At high frequencies, and longer configurations, rapid switching between the source and nearby calibrator is often helpful. See Rapid Phase Calibration and the Atmospheric Phase Interferometer (API) (below).
Rapid Phase Calibration and the Atmospheric Phase Interferometer
Polarization
For projects requiring imaging in Stokes Q and U, the instrumental polarization should be determined through observations of a bright calibrator source spread over a range in parallactic angle. The complex gain calibrator chosen for the observations can also double as a polarization calibrator, provided it is at a declination where it moves through enough parallactic angle during the observation (roughly Dec 15–50 degrees during a several hour track). The minimum condition that will enable accurate polarization calibration from a polarized source, in particular with unknown polarization, is three observations of a bright source spanning at least 60 degrees in parallactic angle (schedule four scans, if possible, in case one is lost); if at all possible, it is strongly recommended that five or more observations covering 100 degrees (or more) of parallactic angle in roughly uniform steps be run. If a bright, unpolarized, unresolved source is available, and known to have very low polarization, then a single scan will suffice to determine the leakage terms. The accuracy of polarization calibration is generally better than 0.5% for small objects as compared to the antenna beam size. At least one observation of 3C286 or 3C138 is required to fix the absolute position angle of polarized emission; 3C48 can be used at frequencies of ~3 GHz and higher, or 3C147 at frequencies over ~10 GHz. Note that 3C138 is variable—the polarization properties are known to be changing significantly over time, most notably at the higher frequencies (for details see Perley and Butler (2013b)).
More information on polarization calibration strategy can be found in the Polarimetry section in the Guide to Observing with the VLA.
VLBI Observations
The VLA can participate in VLBI observations with the VLBA. Presently, this is only allowed in phased array mode (single dish is only available through the VLBA Resident Shared Risk Observing program) with restricted WIDAR correlator configurations. Also note that, currently, P-band cannot be phased. For more details see the VLBI at the VLA documentation. In phased array mode the program TelCal derives the antenna-based delay and phase corrections needed for antenna phasing in real time. This correction is applied to the antenna signals before they are summed, requantized to 2-bits, and recorded in VDIF format on the Mark5C disk at the VLA site. The disk(s) are then transported to Socorro, NM and correlated on the DiFX correlator with other VLBI stations which participated in the observation. Standard VLA data, i.e., correlations between VLA antennas, are also archived in the NRAO science data archive.
Snapshots
The two-dimensional geometry of the VLA allows a snapshot mode whereby short observations can be used to image relatively bright, unconfused sources. This mode is ideal for survey work where the sensitivity requirements are modest.
Single snapshots with good phase stability of strong sources should give dynamic ranges of a few hundred. Note that because the snapshot synthesized beam contains high sidelobes, the effects of background confusing sources are much worse than for full syntheses, especially at 20 cm and longer wavelengths in the D configuration. For instance, at 20 cm, a single snapshot will give a limiting noise of about 0.2 mJy. This level can be reduced by taking multiple snapshots separated by at least one hour. The deconvolution of the data is necessary to remove the effects of background sources. Before considering snapshot observations at 20 cm, users should first determine if the goals desired can be achieved with the existing Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-centimeters survey (FIRST, http://sundog.stsci.edu/top.html) (B configuration) or the NRAO VLA Sky Survey (NVSS, http://www.cv.nrao.edu/nvss/) (D configuration, all-sky).
Shadowing and Cross-Talk
Observations at low elevation in the C and D configurations will commonly be affected by shadowing. It is strongly recommended that all data from a shadowed antenna be discarded. This will automatically be done during filling when using the default inputs with CASA tasks importasdm and importevla. AIPS task UVFLG can be used to flag VLA data based on shadowing, although it will only flag based on antennas in the dataset, and is ignorant of antennas in other subarrays. The CASA task flagdata can also be used to flag data based on shadowing. For more information on shadowing, please see the Antenna Shadowing section in the Guide to Observing with the VLA.
Cross-talk is an effect in which signals from one antenna are picked up by an adjacent antenna, causing an erroneous correlation. This effect is important at low frequencies in compact configurations. Careful examination of the visibilities is necessary to identify and remove this form of interference. The affected data would show time-variable high-amplitude points.
Combining Configurations and Mosaicking
Any single VLA configuration will allow accurate imaging of a range of spatial scales determined by the shortest and longest baselines. For extended and structured objects, it may be required to obtain observations in multiple array configurations. It is advisable that the frequencies used be the same for all configurations to be combined. The ideal combination of arrays results in a uv-plane with all cells equally filled by uv-points. To first order, this can be achieved by using the beam sizes of the individual arrays to inversely scale the on-source integration time. This approach is equivalent to achieving the same surface brightness sensitivity for all arrays on all scales. For the VLA, observations in the different configurations generate beam sizes that decrease by factors of three, i.e., C configuration generates a three times smaller beam than D configuration, B three times smaller than C, and A three times smaller than B. Thus, on-source integrations would increase by about an order of magnitude between each array. Such a drastic increase is very expensive and, in fact, not necessary since some spatial scales are common to more than a single array, which is equivalent to some uv-cells being filled more than others. The best way to fill the uv-plane depends on many factors such as declination of the source, LST time of the observation, and bandwidth.
Experience shows for the VLA that a factor of about three in on-source integration time for the different array configurations works well for most experiments. For example, a 20min on-source time in D, 1hr in C, 3hrs in B, and 9hrs in A should produce a decent map. Using large bandwidths and multi-frequency synthesis will broaden all uv tracks radially and one may need even less array configurations or shorter integration times between the different arrays.
Objects larger than the primary antenna pattern may be mapped through the technique of interferometric mosaicking. The VLA has no limit on the number of pointings for each mosaic. Typically hexagonal, rectangular, or individual pointing patterns are used and the overlap regions will result in an improved rms over each individual pointing. Given the many, potentially short observations, it is important to obey the data rate limits outlined in the Time Resolution and Data Rates Section. On-the-fly (OTF) mosaics, i.e. dumping the data while moving the telescopes across the source, is also available.
Time-variable structures, such as the nuclei of radio galaxies and quasars, cause special, but manageable, problems. See the article by Mark Holdaway in Reference 2 of the Documentation for more information.
Guidelines for mosaicking with the VLA are given in the Guide to Observing with the VLA.
Pulsar Observing
The VLA can be used for several kinds of pulsar observing: phase-binning using the WIDAR correlator, using the phased-array for single-beam pulsar processing in either search or fold modes, or simply standard imaging mode with fast integrations. Any of these types of pulsar observing are considered Resident Shared Risk Observing (RSRO), and participants in this program are expected to work closely with NRAO staff. Of these, phased-array and fast-dump observing are significantly more mature than phase binning. For any questions not addressed here regarding the capabilities of these observing modes, please contact the NRAO Helpdesk.
Phased-array pulsar processing
The "Y" Ultimate Pulsar Processing Instrument (YUPPI) is a suite of software that runs in the correlator backend (CBE) computer cluster and can process a single-beam phased/summed-array data stream for pulsar observations in real time, into either folded profiles or search mode (filterbank) output. Coherent dedispersion can be optionally applied in either mode.
In this mode, the voltage data streams from each antenna are divided into a number of frequency subbands within the correlator, then summed and requantized before being output to the cluster for pulsar processing. The limitation on bandwidth comes primarily from the available network connections between the correlator and cluster. In all cases, a maximum of 64 subbands total can be processed. Depending on the number of bits chosen, this results in the following total bandwidth constraints:
|
Subband bandwidth |
Subband quantization |
Max total bandwidth |
Samplers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 MHz | 8 bits | 2048 MHz | 8-bit |
| 64 MHz | 4 bits | 4096 MHz | 3-bit |
| 128 MHz | 2 bits | 8192 MHz | 3-bit |
| <32 MHz | 8 bits | 64*BWsub | 8-bit |
As described in the VLA Frequency Bands and Tunability section, the 8-bit samplers provide two independently tunable 1 GHz IFs, while the 3-bit samplers provide four tunable 2 GHz IFs.
The pulsar-specific processing is done in real time using the DSPSR software package and, in principle, any processing option supported by DSPSR can be used, although this will be constrained by the real-time computing power available in the cluster. In general, each subband can be divided into an arbitrary (2n) number of channels; 1 (summed), 2 or 4 detected polarization products can be output; and coherent dedispersion can be enabled or not.
Fold mode
In fold mode, the data are averaged modulo a known pulsar ephemeris (provided via a standard TEMPO/TEMPO2 "par file") into pulse profiles. The data can also be folded at a constant topocentric period, for example at 10 Hz to detect the injected noise cal signal. Fold integration times as short as 1 second have been tested. Up to 16384 profile bins can be used. The data are recorded in PSRFITS format using the standard 16-bit data encoding. This means the final output data rate is given by:
Data rate = 2 bytes × Nsubband × Nchannel × Nbin × Npoln / Tint
If the desired data rate exceeds ~25 MB/s, additional testing ahead of time may be required.
Search mode
In search mode, the data are simply detected and averaged over a specified amount of time before being output to disk, resulting in a filterbank data array (power vs time and frequency). Coherent dedispersion at a known DM can optionally be enabled for this. Data can be recorded using 2, 4, 8, 16 or 32 bits, resulting in a final data rate of:
Data rate = (Nbit/8) bytes × Nsubband × Nchannel × Npoln / Tint
The maximum sustained output rate in this mode should be kept less than ~400 MB/s.
Gated or binned visibilities
The WIDAR correlator has the capability to internally integrate (fold) visibilities into 1 or more pulse phase bins. Constraints and trade-offs on number of bins, bin width, pulse period, bandwidth, and integration time are currently not well quantified. This mode is likely to require significant development work to become usable.
Fast-dump visibilities
While not specifically a pulsar mode, standard visibility data can be dumped as fast as 5 ms, which may be sufficient for imaging of slow pulsars. See the Time Resolution and Data Rates section for more details.




Connect with NRAO