The Observations.
Next: The Global Ionosphere Models Up: VLBA SCIENTIFIC MEMO 23 Previous: Background.
The Observations.
RDV11 was observed on 1-2 October 1999 for 24 hours. This was a typical RDV run with 17 antennas delivering data. A total of 84 different sources were observed. The schedule was made with the automatic scheduling mode in SKED, which optimizes the sky coverage over each antenna. There are typically 2 or 3 subarrays in effect at any given time, although there are occasional scans with most or all antennas. The observations were fringe fitted in AIPS using separate files for S and X bands. Then the multiband delays were derived and sent to the special program described above. Only displays from that program will be shown here.
TP015 was observed on 31 March 1999 on the VLBA using the S/X system. The ``target'' sources were 0202+149, 0201+113, 0235+164, 0239+108 and the calibrator was 0229+131. All are taken from the USNO reference frame lists and have absolute positions with formal errors much smaller than 0.1 mas. All are easily strong enough to detect in short integrations in individual bands and to get reasonably high SNR fringe fit results. A cycle of 1.25m dwell time scans (typical total scan length including slew and setup of 1.4m) was used in which 0229+131 was observed every third scan, flanking either 0201+113 and 0202+149 or 0235+164 and 0239+108.
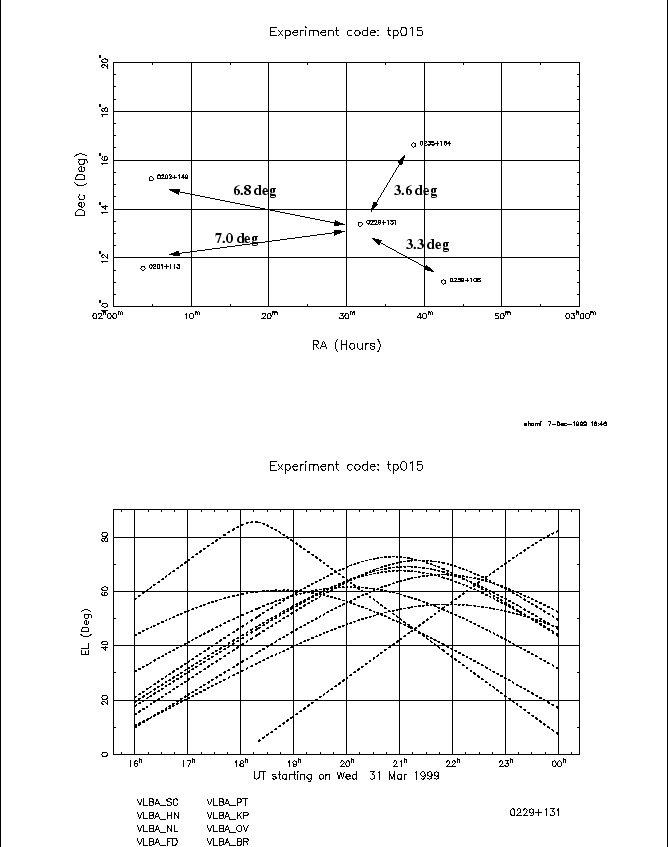 |
The geometry of the observations is shown in Figure 1. The top plot shows the relative positions and separations of the sources. Note that 0239+108 and 0235+164 are both about 7 degrees from 0229+131. This is somewhat farther than our usualy recommended maximum of 5 degrees for a phase reference source on the VLBA. The other two sources are about 3.5 degrees from the reference, which would be reasonable by our usual criteria. The bottom plot of Figure 1 shows the elevations vs. time for 0229+131 for each antenna. Most of the observations are at reasonably high elevations, although sources rise at MK during the run and get near set at SC at the end.
Next: The Global Ionosphere Models Up: VLBA SCIENTIFIC MEMO 23 Previous: Background. Craig Walker
2000-03-16




Connect with NRAO