Custom Type Frequency Sweep Setup
On November 8, 2023, a new Resource Catalog Tool was introduced which changes the way custom resources are created. This section will cover the creation of a custom Frequency Sweep resource. If you have questions or issues, please contact us through the NRAO Science Helpdesk.
Create a Frequency Sweep Resource
After selecting to create a new instrument configuration, the New Resource Wizard pop-up box will appear with several options.
To create a frequency sweep resource select,
- Frequency Sweep
- Array Configuration: This will set the recommended default correlator integration time, which can be changed later if needed.
- Observing Band: Be sure to select the correct observing band since it cannot be changed at a later step.
- Sampler Input Mode: 8-bit or 3-bit, mixed mode can be chosen in the Basebands tab
- Name: This should match the name of the resource entered in the PST.
- Finally, select the Generate button.
Basics Table
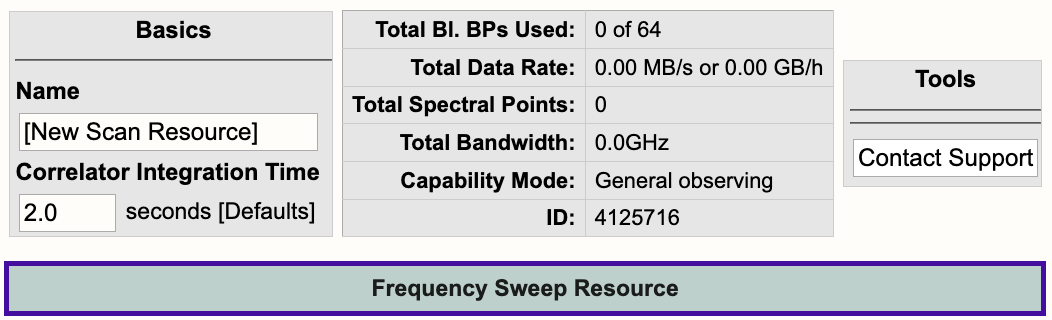
Near the top you will find the Basics info table (see Figure 3.3.4a) were you can change the name of the resource and the correlator integration time.
 |
|
Figure 3.3.4a: Frequency Sweep Basics info table. |
Below is a description of the parameters in the Basics table.
| Name |
Be sure to use unique names for all different resource setups and do not use special characters. |
| Correlator Integration Time (seconds) |
The correlator integration time would have been set when the resource was initially created by selecting one of the array configurations. This can be modified in the table if you do not wish to use a default setting. For more details, refer to the Time Resolution and Data Rates section of the Observational Status Summary (OSS). |
| Total Bl.BPs Used |
This indicates the total baseline board pairs (BlBPs) used, i.e., correlator resources. The starting number will always be zero and will increase as lines and continuum subbands are added and when more baseline board pairs are used per line. |
| Total Data Rate |
The data rate of the resource will increase as lines and continuum subbands are added. Keep in mind the minimum and maximum data rates: Time Resolution and Data Rates. |
| Total Spectral Points |
The total spectral points will increase as the number of requested BlBPs increases. For a more detailed explanation, refer to the Recirculation vs Baseline Board Pairs section. |
| Total Bandwidth (GHz) |
This will display the sum of all subband bandwidths across all basebands in GHz. |
| Capability Mode |
The will display the capability mode of a resource, e.g., general, shared risk, or resident shared risk observing. This will depend on the total data rate and certain other settings described in the OSS. |
| ID |
This is the resource ID. |
| Contact Support |
Selecting this button will allow you to contact the NRAO Science Helpdesk. |
Lines Tab
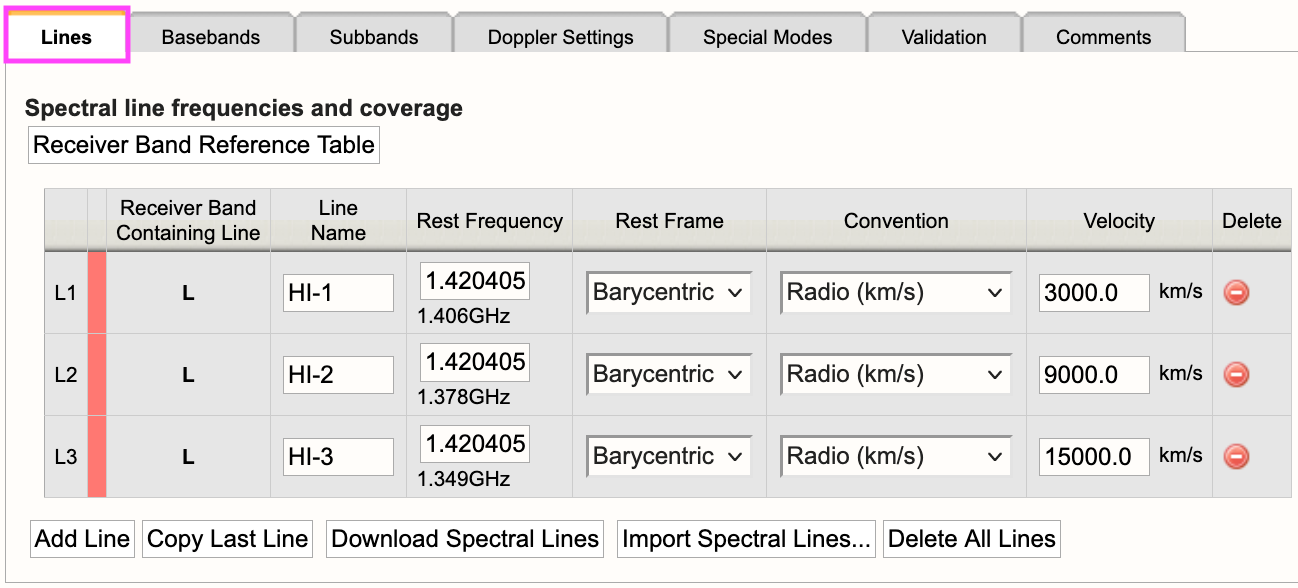
In the Lines tab (Figure 3.3.4b), you may either enter the line information one-at-a-time by selecting Add Line or import a text file containing a list of lines by selecting:
Import Spectral Lines → Browse (select the txt file containing the lines you want to import/upload) → Upload → Done (if using Firefox)
(Note, if you are using Firefox you will be required to select the Done button after selecting Upload to complete the import. Otherwise, selecting Upload will complete the import.)
 |
|
Figure 3.3.4b: Frequency Sweep Lines tab. |
For each line you will need to provide the following information:
| Line Name |
Do not use special characters and keep the name relatively short. |
| Use Line in Automated Setup (all/none) |
You may choose which lines are used in the automated setup. This means you can upload a set of lines and only use some of them or use this option as a way to partially automate/manually setup your resource. |
| Rest Frequency |
Rest frequency of the line you wish to observe in GHz. |
| Rest Frame |
LSR, Topocentric, Barycentric, Geocentric |
| Convention |
Radio (km/s), Optical (km/s), Redshift (Z), Relativistic (km/s) |
| Velocity (km/s) |
The line-of-sight velocity at which the line should be observed. |
Below is an example of a line text file for a Frequency Sweep resource. For more details, refer to the OPT manual. Note, you may also use the same syntax you would use for a spectral line text file. This means you may export a set of lines from an existing resource in the RCT-observing (this is the RCT used in conjunction with the OPT when setting up observations).
#Line name; Rest frequency; Rest frame; Velocity convention; Velocity; Minimum range; Channel separation; Polarization products
HI-1; 1.420405751GHz; Barycentric; Radio; 3000.0km/s; 100.0km/s; 1.0km/s; FULL
HI-2; 1.420405751GHz; Barycentric; Radio; 9000.0km/s; 100.0km/s; 1.0km/s; FULL
HI-3; 1.420405751GHz; Barycentric; Radio; 15000.0km/s; 100.0km/s; 1.0km/s; FULL
Basebands Tab
Set the baseband center frequencies and sampler input mode.
Subbands Tab
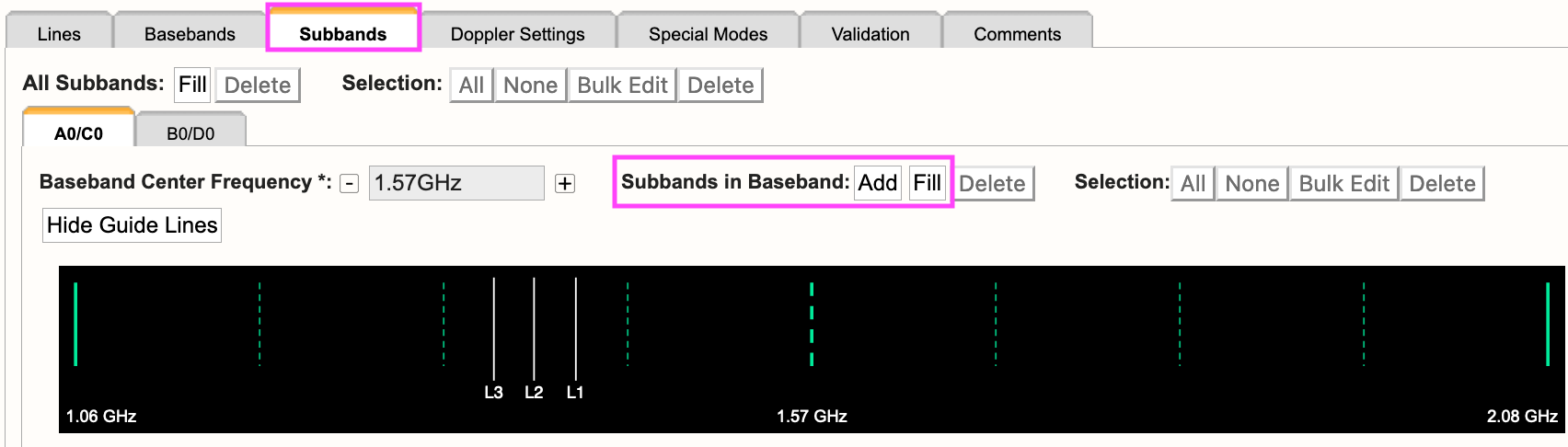
The lines added to the Lines tab will appear as a guide for placing continuum subbands with more correlator resources, e.g., BlBP stacking and recirculation. For more details on stacking BlBPs and increasing recirculation, please refer to the Recirculation vs Baselineboard Pairs section.
For each baseband, continuum subbands can be added one-at-a-time by selecting Add or use the recommended Fill button at the "Subbands in Basebands" level (see Figure 3.3.4c). Manually adding subbands one-at-a-time will require the user to select the Add button, then select the central frequency range of each continuum subband by choosing the desired range in the drop-down menu located in the subbands table. With either option, bulk filling the subbands or manually adding the subbands, the user can edit individual subbands as needed.
 |
|
Figure 3.3.4c: Subbands tab. |
Selecting Fill, the user will be presented with a pop-up box containing the following parameters:
| Bandwidth |
This defines the bandwidth of each continuum subband. |
| Number of Subbands |
The maximum number of subbands per baseband will vary depending on the sampler mode (3-bit or 8-bit) and how many baseline board pairs have been used so far by the generated spectral lines. |
| BlBPs |
Number of baseline board pairs to stack per subband. |
| Polarization |
Full (RR, LL, RL, and LR), Dual (RR and LL), or single (RR or LL) |
| Array Summing |
None should be used for frequency sweep resources. |
| Recirculation |
This can be utilized per subband to increase the resolution without increasing the number of BlBPs, i.e., correlator resources. |
| Place first subband in Grid |
The default is to start at the #2 subband. You may change this to start at a different subband, e.g., #1. |
Doppler Settings Tab
This is optional. For more details, refer to the Doppler Tuning Tab portion of the Spectral Line Setup section.
Special Modes Tab
RFI blanking can be enabled for the entire resource. For more details, refer to the RFI Blanking section.
Validation Tab
If the resource does not validate and it's not clear why, contact the NRAO Science Helpdesk via the RCT. Contacting us via the RCT will append a log file to the ticket so we can take a deeper dive into the resource errors.
Comments Tab
You may provide comments as notes to yourself for future reference.




Connect with NRAO