Linking SBs
Once the scheduling blocks (SBs) are created, you may have some conditional constraints for the execution of their observation(s). Linking SBs is done at the program block (PB) level (as seen in Figure 4.8.1). The PB should contain at least two SBs which are listed with an index number in the first column of the first table in the Scheduling Blocks section.
The concept of linking SBs will allow you to specify alternate SBs within a PB that can be scheduled. For example, in a simple case, you might specify that either SB "1" or SB "2" could be run depending on which LST start range fits best into the schedule. Scheduling priorities are also changed when conditional constraints are specified in a PB. For linked SBs the basic types with their implied priorities are:
| Conditional Constraint | Priority within Linked Blocks | |
| Only one of the blocks | → | LST start range closest to schedule start |
| Total number of executions of the block | → | LST start range closest to schedule start |
| Any of the blocks | → | LST start range closest to schedule start |
| Total hours not to exceed a limit | → | Scheduling Priority Order |
Important Notes
- If an SB is removed (i.e., cut from the left-hand column list), the indexing of the SBs will be re-numbered. Therefore, all linked SBs should be double checked in case the re-numbering of the SB index affected those linked SBs. If those linked SBs received new indexes, then the constraint should be removed and a new constraint be added.
- If a linked SB is unsubmited, the conditional format will be automatically removed. Therefore, be sure to re-link the SBs.
- The SBs within a format statement are evaluated based on the LST start time, with a preference given to the SB in the list that has the earliest SB ID.
- Once a conditional format has been met, the Observation Scheduling Tool (OST) will put the linked SB(s) on hold. Then, we have a cron job that runs every morning around 08:00MT which will expire the SB(s) placed on hold and send an email to the PI, co-I's, and the VLA schedulers. SBs that have been placed on hold and/or expired cannot be selected by the OST for observing.
- Adding no conditions at all, i.e., no linked SBs, is a valid option. We do not require SBs to be linked in order to be considered for observation.
How to Link SBs
To link SBs, select the Edit Constraints button to enter the constraints in the Linked Scheduling Blocks interface above the table of SBs. Constraints are based on the index number of the SB and take the form of selecting those SBs and comparing it to a time or number of execution limit. (Fly-over help is available for all of the fields.)
Once all constraints are satisfactory, the conditions have to be communicated to the system by selecting Stop Editing Constraints. This will notify the on-line system that conditions have been specified and will change the Stop Editing Constraints button into an Edit Constraints button for additional future editing if necessary.
|
|
|---|
|
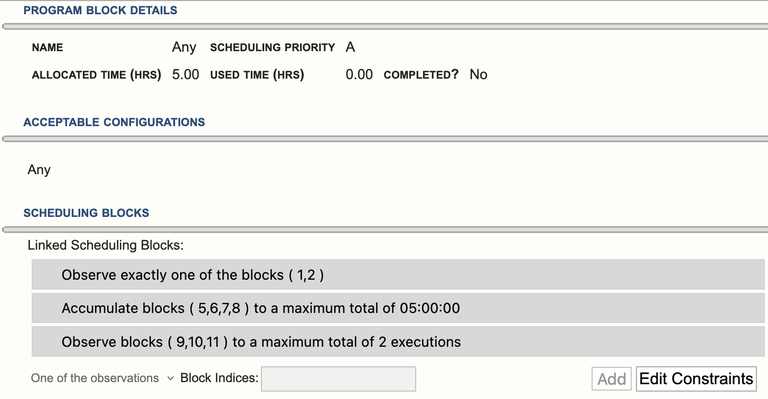
Figure 4.8.1: Examples of linked SBs. |
Common Examples as Seen in Figure 4.8.1
Observe exactly one of the blocks (1,2)
- This is the most commonly used conditional format. The logic is, observe only one of the two SBs. We often recommend this for observations utilizing two LST start ranges to avoid observing sources transiting too close to zenith.
- Another use case is with multiple SBs so only one of several SBs will be observed. For example, several SBs are created for different weather conditions, i.e., don't run the SB with high-frequency resources when the weather is not suitable, but instead of waiting for the weather to improve, run a different SB with more relaxed weather constraints.
Accumulate blocks (5,6,7,8) to a maximum total of 05:00:00
- This can be used for a set of SBs of varying lengths with appropriate counts/repeats to accumulate a certain amount of time. For example, a 5.0hr SB could be submitted and to help improve chances of getting data, three additional SBs of varying lengths and counts could be submitted and linked to the 5.0hr SB. If the 5.0hr SB is not easily schedulable in the dynamic queue, an accumulation of the shorter SBs could be selected instead.
Observe blocks (9,10,11) to a maximum total of 2 executions
- This is similar to the previous example. Three SBs using different LST start ranges each with a count of 2, yet only 2 executions of this set of SBs should be completed.




Connect with NRAO